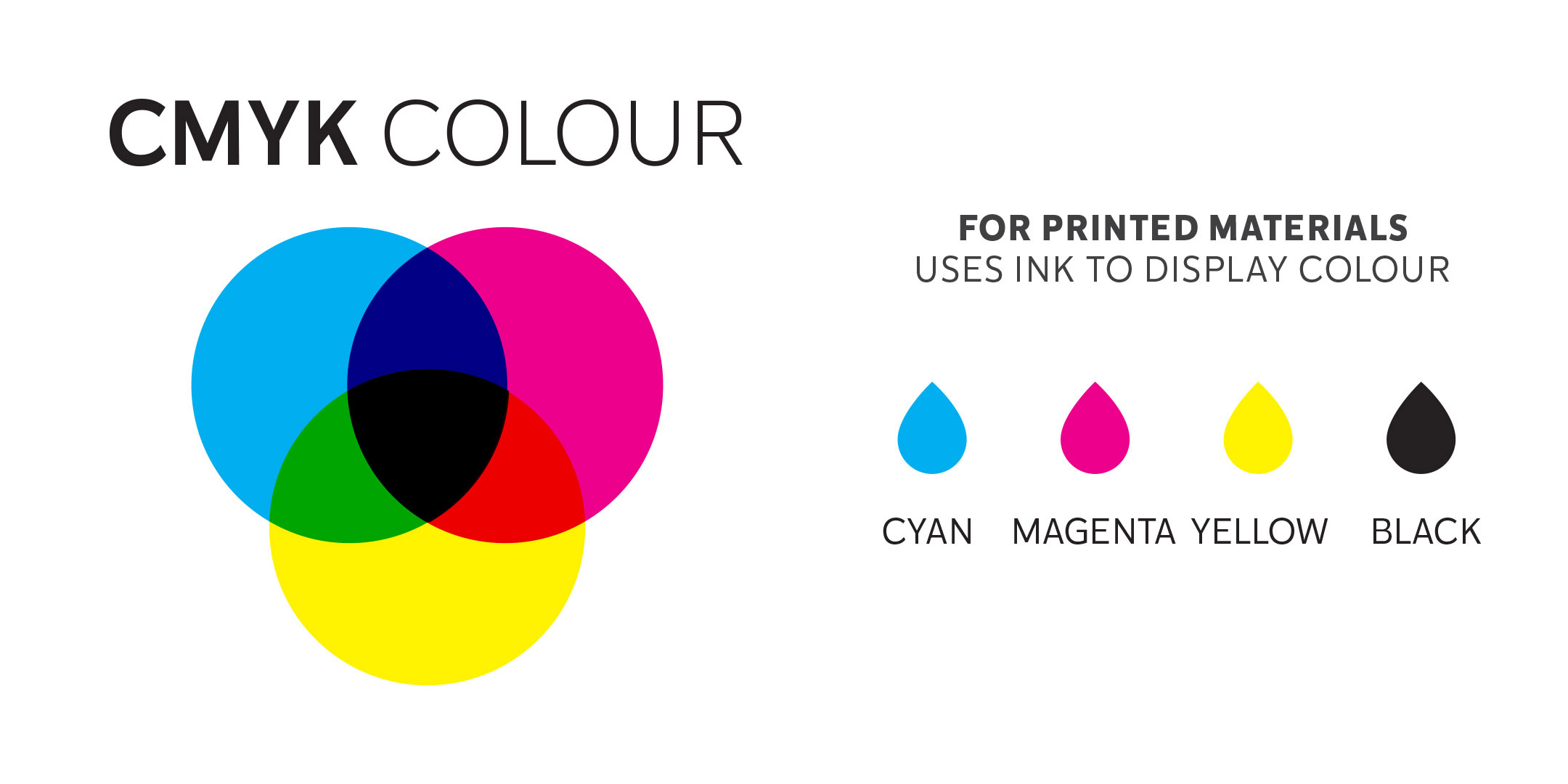
Different design projects require different colour systems depending on how they are being produced. In a brand guide for example, there will be usually be CMYK and RGB values for the different brand colours. What’s the difference between them and why do we need both?
CMYK is created with ink
A full range of colours are created by adding physical Cyan (bright blue) Yellow, Magenta (bright pink) and Black inks on white paper.
Any project that will be physically printed with ink rather than on a digital screen.
CMYK values range between 0 – 100.
No covering of ink = 0
100% covered of ink = 100
Black (completely covered in ink) has a value of:
C: 100
M: 100
Y:100
K:100
While white (no ink) has a value of:
C: 0
M: 0
Y:0
K:0
Please note: There is a minimum and maximum value of ink coverage for the best printing result. General guidelines are not going below 10% for minimum ink coverage or over 280 -300% for maximum ink coverage but will depend on the type of paper or ‘stock’ being used.
Some colours can’t be reproduced using the CMYK system (such as fluorescent orange or reflex blue) . Another option is a“spot colour “ using special inks in the Pantone colour matching system.
RGB is created with light
Starting with a black digital screen Red, Green and Blue light are added to create colour.
Anything that is created electronically for a digital screen uses RGB colour.
RGB values have a range between 0 – 255 for each colour denoting the amount of light added.
Black (no light) for example, has a RGB value of:
R: 0
G: 0
B: 0
Whereas white (maximum light) has the highest value for red, green and blue lights, creating white.
R: 255
G: 255
B: 255
Please note: Some colours that look bright and vibrant on screen are hard to recreate physically with CMYK ink. Especially bright orange and some light turquoise blues.
Feel free to get in touch if you have any colour queries.